Abstract
Social media platforms are essential outlets for expressing opinions, providing a valuable resource for capturing public viewpoints via text analytics. However, for many users, passive browsing is their preferred mode of interaction, leading to their perspectives being overlooked by text analytics methods. Meanwhile, social media polls have emerged as a practical feature for gathering public opinions, allowing post authors to pose questions with pre-defined answer options for readers to vote on. To broaden the benefits of polls for posts without them, this article explores the automatic generation of a poll from a social media post by leveraging cutting-edge natural language generation (NLG) techniques. However, existing NLG techniques, primarily developed for general-domain texts, may be ineffective when applied to noisy social media data, which often feature implicit context-question-answer relations. To tackle these challenges, we enrich a post context with its comments and propose a novel unified poll generation framework called UniPoll. It employs prompt tuning with multi-objective optimization to bolster the connection exploration between contexts (posts and comments) and polls (questions and answers). Experimental comparisons on a large-scale Chinese Weibo dataset show that UniPoll significantly outperforms T5, the state-of-the-art NLG model, which generates question and answer separately. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative analyses further underscore the superiority of UniPoll through various evaluation lenses.
Model
UniPoll harnesses the power of multi-objective optimization via task prompt tuning to balance the intricate relationships between contexts, questions, and answers. This innovative approach ensures a harmonious and contextually relevant poll generation process, setting new standards for NLG in social media.
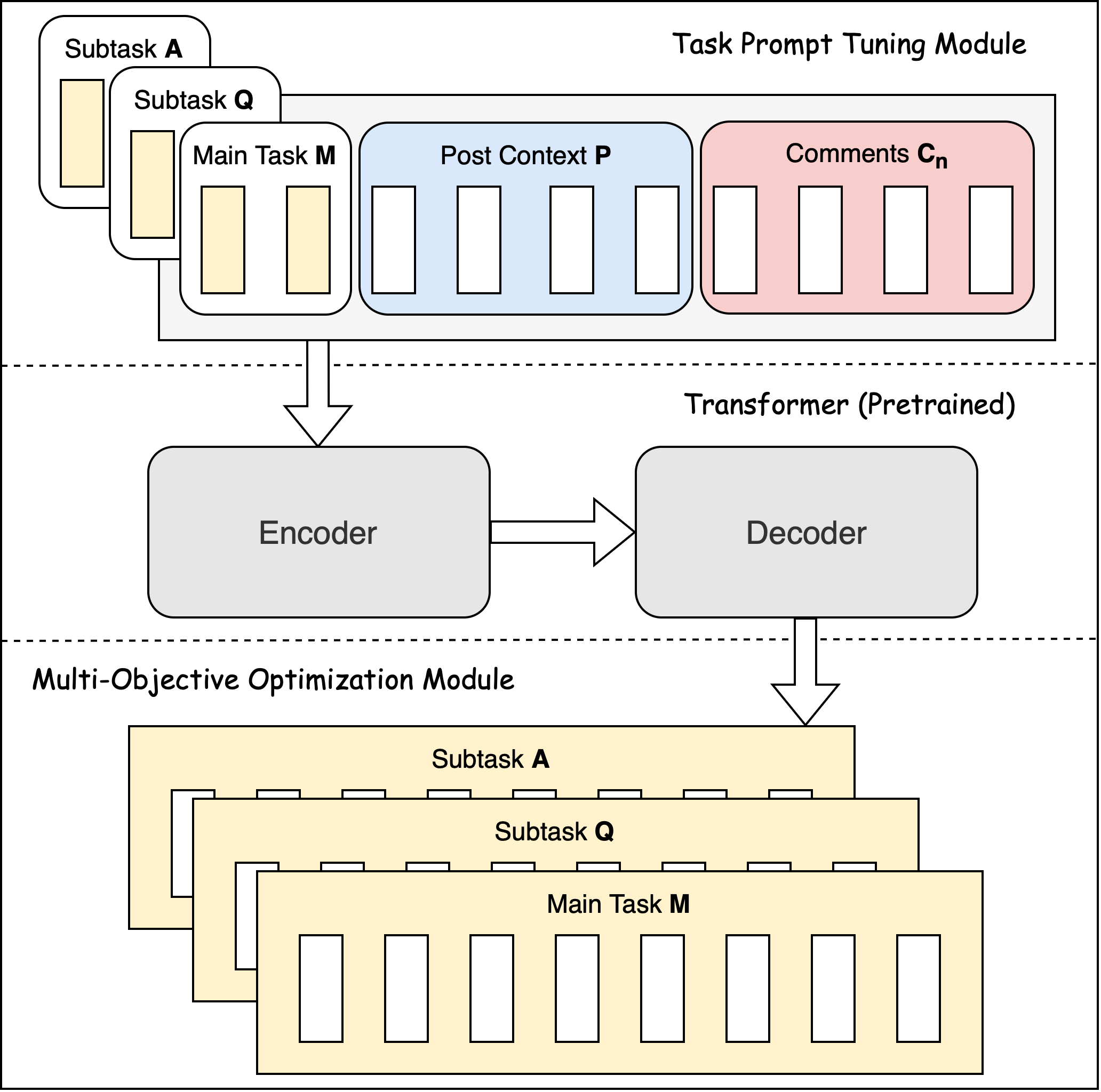
The architecture of UniPoll.
Data
We evaluate our proposed UniPoll model on the WeiboPolls dataset, currently the only available benchmark dataset for poll generation. The WeiboPolls dataset consists of 20,252 poll question pairs gathered from the Chinese social media platform Weibo. Each sample in the dataset includes the context of a post with its comments and an author-created poll with a question and a set of poll answers.
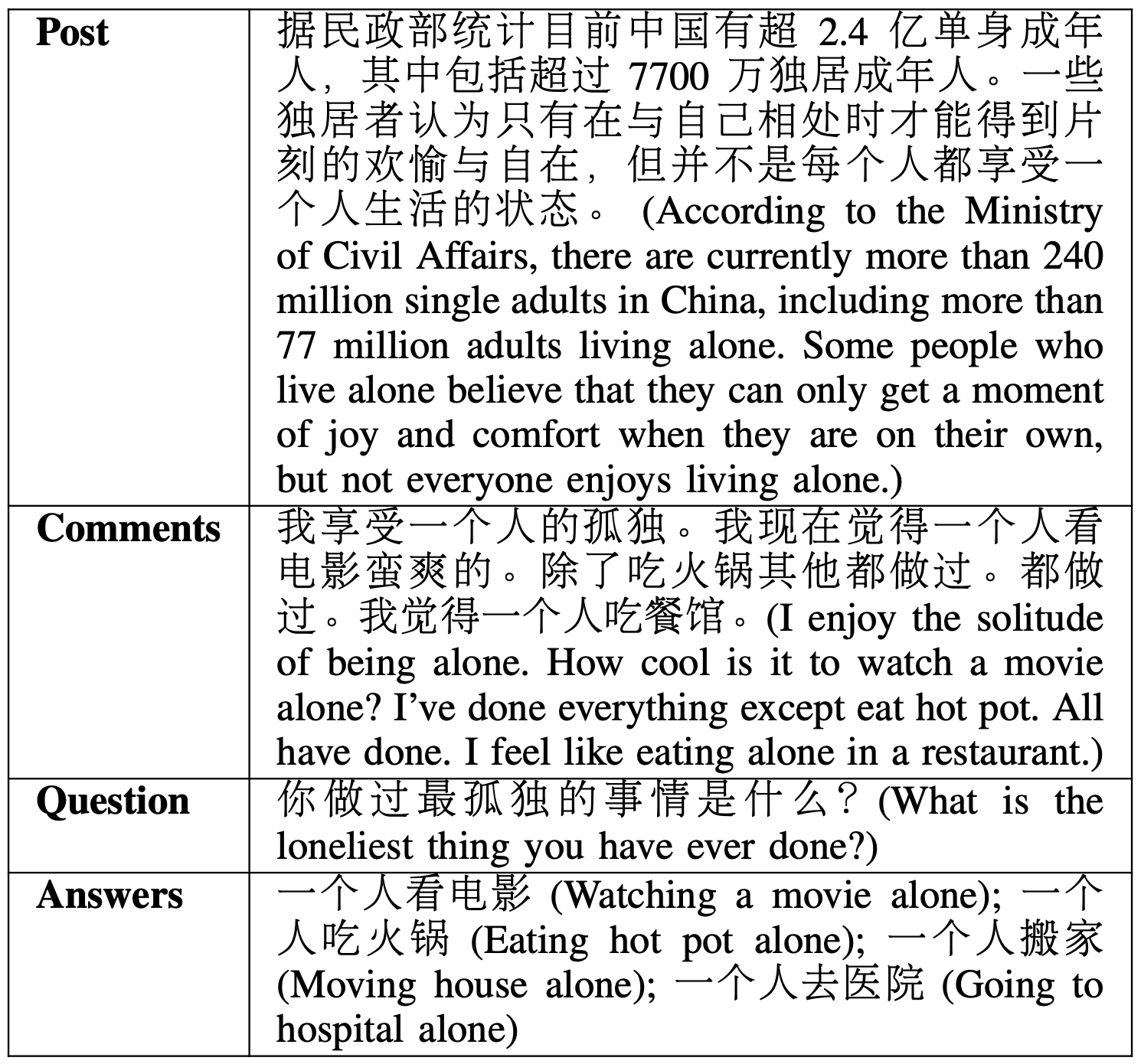
An Exemplary Weibo Poll from the WeiboPolls Dataset.
Main Results
UniPoll significantly outperforms all baselines and previous state-of-the-art models in both automated (left) and human (right) scoring. For example, UniPoll achieves a ROUGE-1 score of 47.92, outperforming T5 and DUAL DEC with scores of 45.33 and 34.98 respectively. In the human evaluation, UniPoll achieves the highest scores across different metrics, indicating its effectiveness in generating human-preferred social media polls.
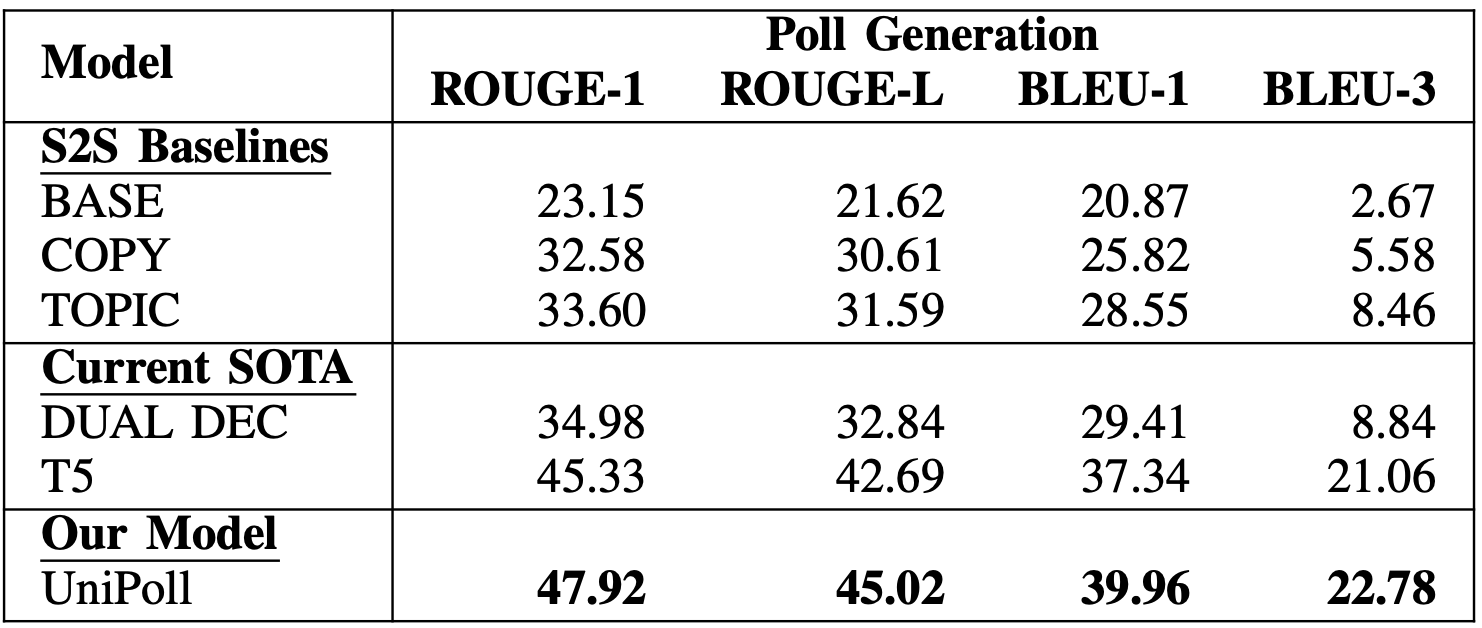
Automatic Evaluations Results for Poll Generation.
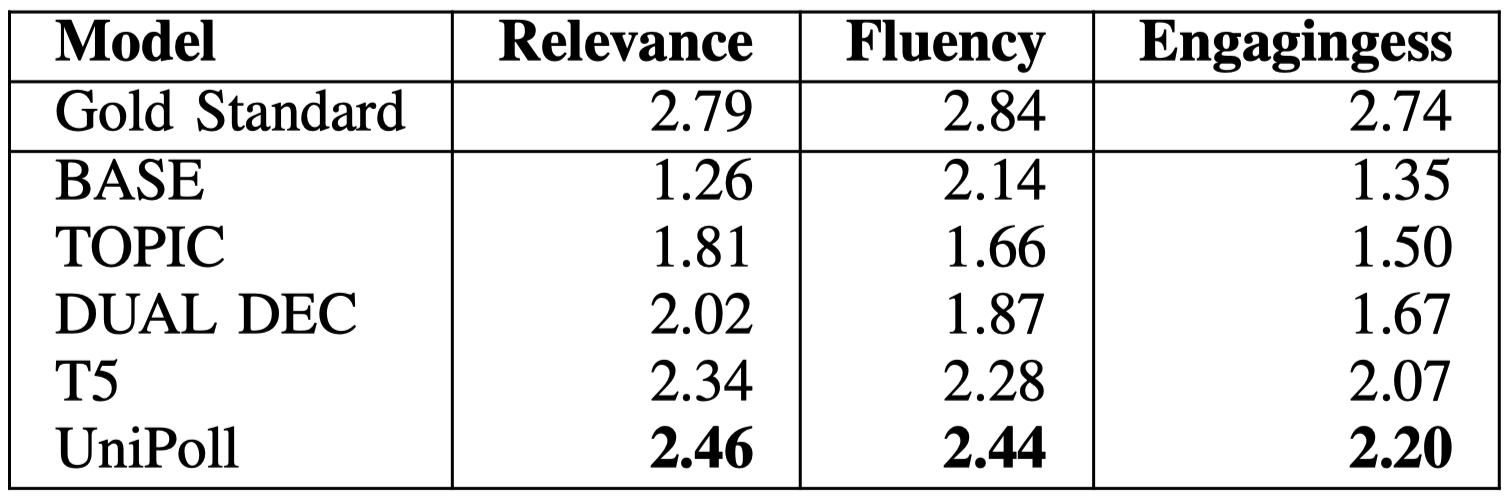
Human Evaluation Results for Poll Generation.
Case Study
UniPoll excels compared to other poll generation models due to its ability to create context-specific, engaging polls. UniPoll's focus on context-question-answer relations results in high-quality polls that stand out, while other models like T5, ChatGPT, and NewBing often produce more general, inconsistent, or less engaging polls.

Case Study.